Aug 21, 2024
SEO Guide for Dummies - A Tutorial For the Rest of Us
SEO Guide for Dummies - A Tutorial For the Rest of Us
SEO Guide for Dummies - A Tutorial For the Rest of Us
SEO Guide for Dummies - A Tutorial For the Rest of Us
Start your SEO journey with our SEO Guide for Dummies. Learn step-by-step SEO principles, keyword research, and optimization techniques tailored for beginners
Start your SEO journey with our SEO Guide for Dummies. Learn step-by-step SEO principles, keyword research, and optimization techniques tailored for beginners
Start your SEO journey with our SEO Guide for Dummies. Learn step-by-step SEO principles, keyword research, and optimization techniques tailored for beginners
Start your SEO journey with our SEO Guide for Dummies. Learn step-by-step SEO principles, keyword research, and optimization techniques tailored for beginners

Finley Cope
Finley Cope
Finley Cope
Finley Cope
If you're a small business owner just stepping into the world of digital marketing, you've probably heard about SEO. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing your website so that it appears higher in search engine results, attracting more organic (non-paid) traffic. While SEO might seem intimidating at first, it’s a crucial tool for growing your online presence and driving business success.
This guide is designed as an easy-to-understand introduction to SEO, perfect for beginners. We’ll walk you through the basics, explain the key principles of SEO, and provide you with a step-by-step manual to get started. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation in SEO and be ready to start optimizing your own website.
What Is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of making your website more attractive to search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. When your site is optimized, search engines can better understand your content, index your pages, and rank your site higher in search results for relevant queries.
Key Components of SEO
On-Page SEO: Refers to the elements on your website that you can control, such as content, title tags, meta descriptions, and images.
Off-Page SEO: Involves activities outside your website that impact your rankings, such as backlinks from other websites, social media marketing, and guest blogging.
Technical SEO: Focuses on the backend of your website, including site speed, mobile-friendliness, and proper use of robots.txt and sitemaps.
Why Is SEO Important?
In today’s digital age, most consumers start their purchasing journey with an online search. If your website doesn’t appear on the first page of search results, you’re missing out on valuable traffic and potential customers. SEO is important because it helps your website get discovered by search engines, making it easier for customers to find you.
Benefits of SEO
Increased Visibility: Higher rankings mean more visibility, leading to increased traffic to your website.
Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank high in search results are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
Cost-Effective: Unlike paid advertising, organic traffic generated through SEO is free, making it a cost-effective strategy for small businesses.
Long-Term Results: While SEO takes time to show results, the benefits are long-lasting, providing continuous traffic and leads over time.
SEO 101: Ensuring Google Can Index Your Site
Before diving into more advanced SEO techniques, it’s crucial to ensure that your website is accessible to search engines. If search engines can’t find and index your site, all other SEO efforts will be in vain.
Step 1: Create and Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines understand your site’s structure and index it more efficiently.
How to Create a Sitemap: Most website platforms like WordPress or Shopify automatically generate a sitemap. If not, you can use tools like Screaming Frog or Google XML Sitemaps to create one.
Submitting Your Sitemap: Once your sitemap is ready, submit it to Google Search Console. This tells Google to crawl and index your website.
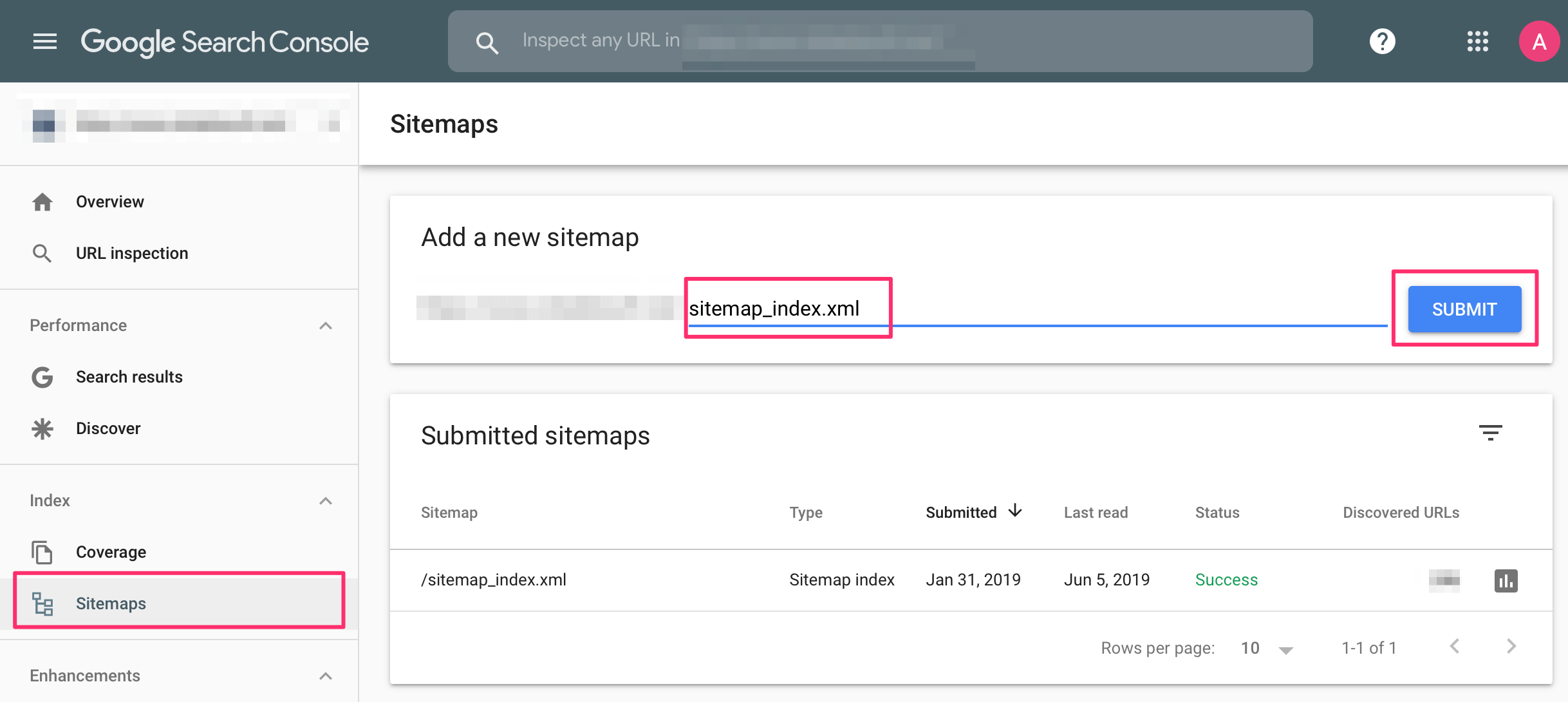
Step 2: Check Your Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is a simple text file that tells search engines which pages on your site they should or shouldn’t crawl. Ensure that this file is correctly configured to avoid accidentally blocking important pages from being indexed.
How to Access Your Robots.txt File: You can find this file at the root of your domain (e.g., www.yoursite.com/robots.txt). Check it to ensure that it’s not disallowing any critical pages.
Step 3: Ensure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
With more than half of all web traffic coming from mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your site is optimized for mobile users. If not, consider switching to a responsive design that automatically adjusts to different screen sizes.
Keyword Research: The Foundation of SEO
Keywords are the phrases that users type into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing these search terms to understand what your target audience is searching for.
Step 1: Identify Relevant Keywords
Start by brainstorming a list of words and phrases related to your business. These should include terms that describe your products or services, as well as any related topics your customers might be interested in.
Tools for Keyword Research: Use ClimbSEO's Keyword Research Tool to find out how often these keywords are searched and how competitive they are. Look for keywords with a high search volume but low competition.
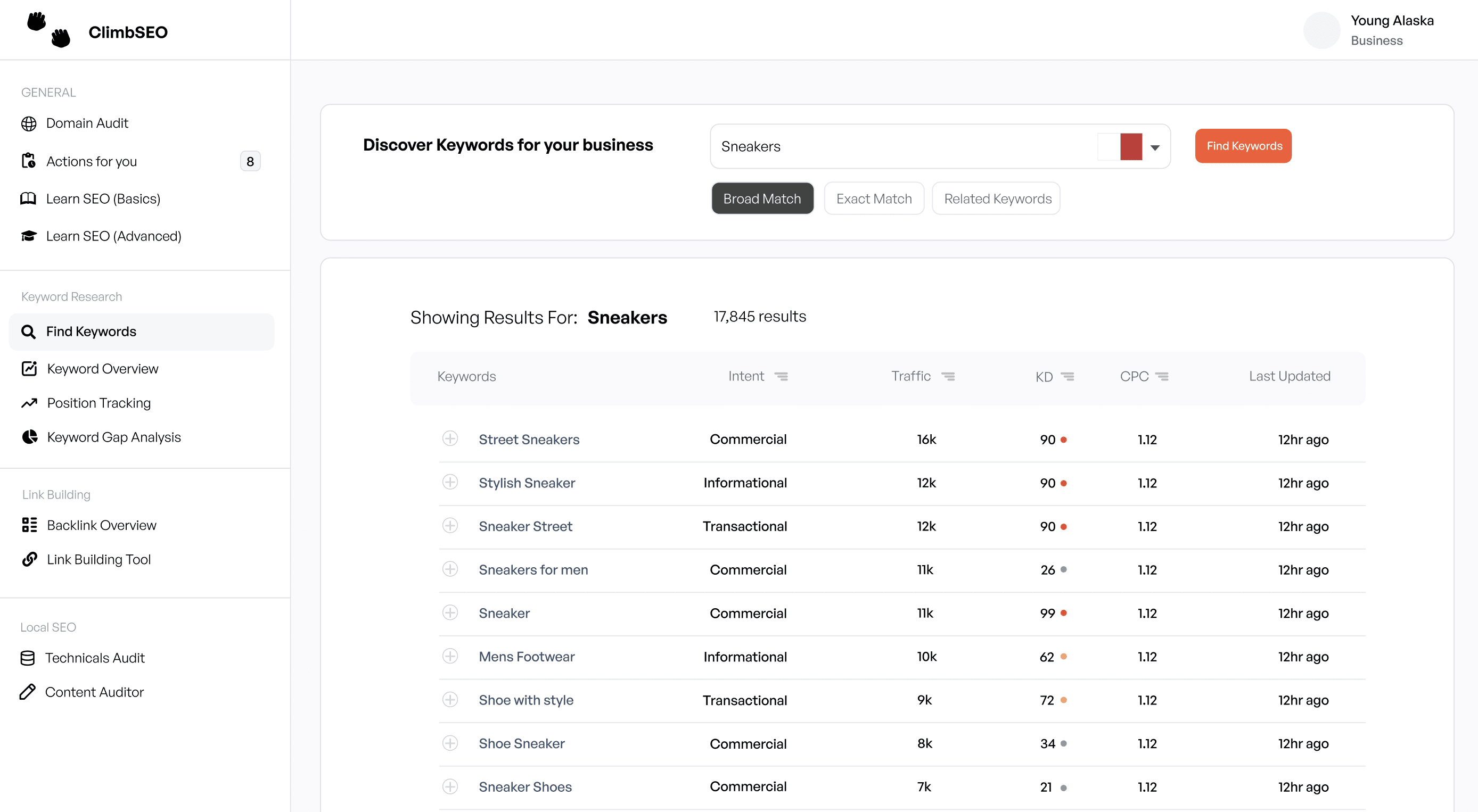
Step 2: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that users are more likely to type when they’re closer to making a purchase. For example, instead of targeting “shoes,” a long-tail keyword would be “women’s running shoes for flat feet.”
Why Long-Tail Keywords Matter: They may have lower search volumes, but they’re also less competitive and often result in higher conversion rates because they match user intent more precisely.
Step 3: Analyze Competitor Keywords
Understanding which keywords your competitors are targeting can provide valuable insights. ClimbSEO's Competitor gap analysis tool helps to see which keywords are driving traffic to their websites and identify any gaps in your own keyword strategy.
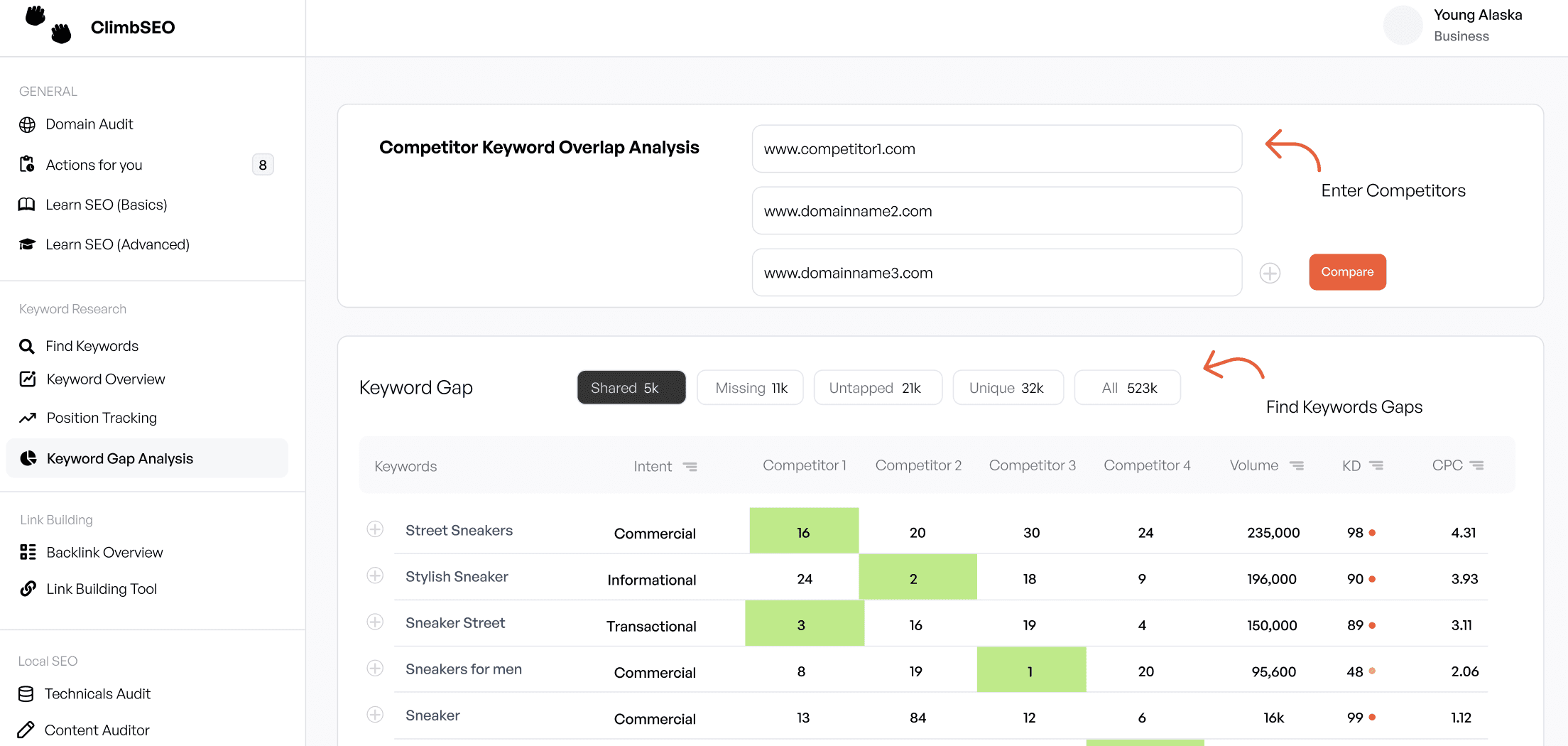
Content: The Heart of SEO
Once you’ve identified your keywords, the next step is to create content that will rank for those keywords. Content is the foundation of SEO because it’s what search engines use to understand your site and decide where it should rank.
Understand What Searchers Want to See for a Query
Before creating content, it’s essential to understand search intent. This means figuring out what users are actually looking for when they type in a particular keyword.
Types of Search Intent:
Informational: The user is looking for information or answers to a question.
Navigational: The user is trying to find a specific website or page.
Transactional: The user is looking to make a purchase or take a specific action.
How to Match Search Intent: Once you understand the intent behind a keyword, create content that directly answers the user’s query. For example, if the keyword is “how to tie a tie,” a step-by-step guide with images or a video would be ideal.
Create Content That’s the Best of Its Kind
To rank well, your content needs to be better than what’s already out there. This doesn’t just mean writing more words; it means providing more value to the reader.
How to Create High-Quality Content:
Be Comprehensive: Cover all aspects of the topic in detail.
Use Visuals: Include images, infographics, and videos to make your content more engaging.
Cite Reliable Sources: Linking to credible sources can enhance your content’s authority.
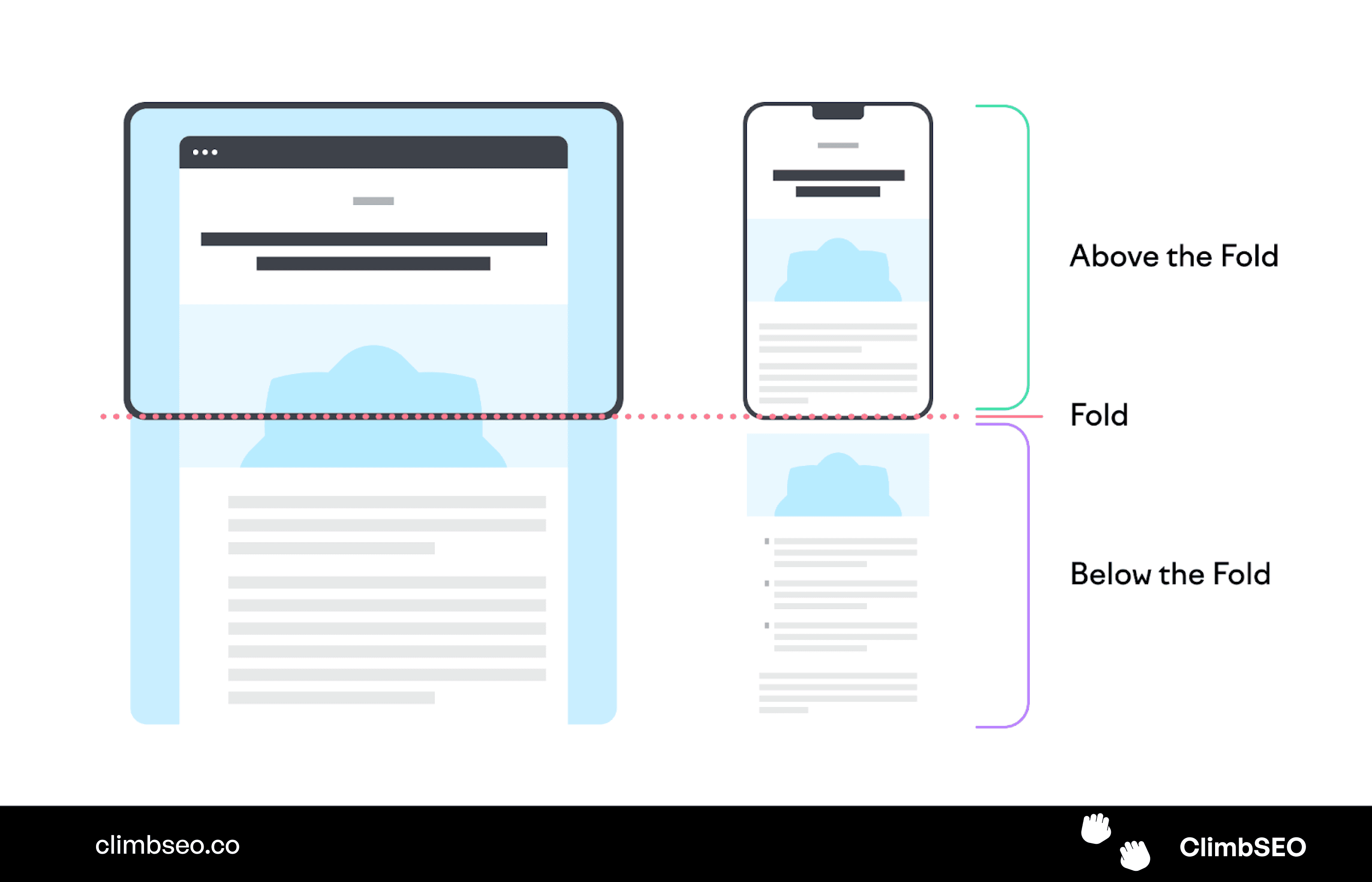
Optimize Your Above-the-Fold Section
The above-the-fold section is the part of your webpage that users see without scrolling. It’s crucial to optimize this area because it’s the first thing visitors (and search engines) see.
Tips for Optimization:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Make sure your main keyword is in the headline or the first paragraph.
Use a Compelling CTA: A strong call-to-action (CTA) encourages users to stay on your page and explore further.
Ensure Fast Load Times: Slow load times can lead to higher bounce rates. Compress images and use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up your site.
User Experience: Keeping Visitors Engaged
Search engines like Google consider user experience (UX) as a ranking factor. If users have a positive experience on your site, they’re more likely to stay longer, which signals to search engines that your content is valuable.
Use Enticing CTAs
A CTA is a prompt that encourages users to take a specific action, such as “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up.” Effective CTAs are clear, compelling, and relevant to the user’s needs.
How to Create Effective CTAs:
Be Specific: Instead of “Click Here,” use “Download the Free Guide” or “Start Your Free Trial.”
Create Urgency: Phrases like “Limited Time Offer” or “Get It Now” can motivate users to act quickly.
Place Strategically: Place CTAs in prominent positions where users are most likely to see them, such as at the end of a blog post or in the middle of a product page.
Avoid Walls of Text
Large blocks of text can be intimidating and difficult to read. Break up your content into smaller paragraphs, use headings and subheadings, and incorporate bullet points and numbered lists to make it more digestible.
Tips for Readable Content:
Use Short Paragraphs: Aim for 2-3 sentences per paragraph.
Add White Space: Don’t overcrowd your pages; use white space to give your content room to breathe.
Use Images: Visual elements can help break up text and keep readers engaged.
Use Listicles, Bullets, and Numbered Lists
Listicles and bullet points are effective ways to present information because they’re easy to scan. Users can quickly find the information they’re looking for without having to read through large blocks of text.
Benefits of Lists:
Improved Readability: Lists make it easier for users to process information.
SEO Advantage: Search engines often feature listicles and bullet points in “People Also Ask” and featured snippets.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing Individual Pages
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This includes optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content for your target keywords.
Title Tags
The title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO elements. It’s the clickable headline that appears in search engine results and tells both users and search engines what the page is about.
Best Practices for Title Tags:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Place it near the beginning of the title.
Keep It Under 60 Characters: This ensures it doesn’t get cut off in search results.
Make It Compelling: Use action words and numbers to make your title more enticing (e.g., “10 Easy Tips to Improve Your SEO”).
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a brief summary of a page’s content that appears below the title tag in search results. While it doesn’t directly impact rankings, a well-written meta description can improve your click-through rate (CTR).
How to Write Effective Meta Descriptions:
Include Your Primary Keyword: This helps users quickly understand the relevance of your page.
Keep It Concise: Aim for 150-160 characters.
Use a Call-to-Action: Encourage users to click with phrases like “Learn More,” “Get Started,” or “Read On.”
Heading Tags
Heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are used to structure your content and make it easier for users to read. They also help search engines understand the hierarchy of your content.
Tips for Using Heading Tags:
Use Only One H1 Tag: This should be the main title of your page.
Incorporate Keywords: Use relevant keywords in your H2 and H3 tags to reinforce your content’s topic.
Maintain Logical Structure: Ensure your headings follow a logical order, with H1 as the main title and subsequent headings as subtopics.
Page URLs
A clean, descriptive URL structure can improve both user experience and search engine rankings. URLs should be simple, easy to read, and include your target keywords.
Best Practices for URLs:
Keep It Short: Shorter URLs are easier to remember and share.
Include Keywords: Make sure your primary keyword is part of the URL.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Avoid using underscores or spaces.
Images
Images are an essential part of any webpage, but they also need to be optimized for SEO. This includes using relevant file names, alt text, and compressing images for faster load times.
How to Optimize Images for SEO:
Use Descriptive File Names: Rename your image files to include relevant keywords (e.g., “blue-widgets.jpg” instead of “IMG_1234.jpg”).
Add Alt Text: Alt text helps search engines understand what the image is about and improves accessibility for users with visual impairments.
Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without compromising quality, improving page load times.
Adding Links from Other Pages on Your Site
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and can also pass authority from one page to another.
Best Practices for Internal Linking:
Use Descriptive Anchor Text: The clickable text of the link should describe what the linked page is about.
Link to Relevant Content: Only link to pages that are relevant to the topic at hand.
Keep a Logical Flow: Ensure that the links guide users naturally through your content.
Link Building: Strengthening Your Site’s Authority
Link building is the process of acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your own. These links are like votes of confidence from other sites, signaling to search engines that your content is trustworthy and valuable.
1. Build Links from Associations, Suppliers, and Connected Businesses
One of the easiest ways to start building links is by reaching out to associations, suppliers, and businesses you’re connected with. They may be willing to link to your website on their “Partners” or “Resources” pages.
How to Approach Link Building:
Create a List: Identify all the associations, suppliers, and partners you work with.
Reach Out: Send a polite email asking if they’d be willing to add a link to your website.
Offer Something in Return: You could offer to feature them on your site as well, making it a mutually beneficial exchange.
2. Submit Your Site to Quality Directories
Online directories can be a valuable source of backlinks, especially if they are well-respected in your industry. However, avoid low-quality directories that might be considered spammy by search engines.
Best Practices for Directory Submission:
Choose Reputable Directories: Focus on directories that are relevant to your industry and have a strong reputation.
Fill Out Your Profile Completely: Ensure that your business name, address, phone number, and website are correctly listed.
Monitor Your Listings: Regularly check your listings to ensure that the information remains accurate and up-to-date.
3. Use HARO to Earn Links from the Press
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) is a platform that connects journalists with sources for their stories. By responding to relevant queries, you can earn high-quality backlinks from authoritative media outlets.
How to Use HARO:
Sign Up: Register as a source on HARO and select the categories relevant to your business.
Monitor Queries: You’ll receive daily emails with queries from journalists looking for sources.
Respond Promptly: When you see a relevant query, respond quickly with valuable insights or expertise. If the journalist uses your information, they’ll often include a link to your website in their article.
Technical SEO: Optimizing Your Site’s Backend
Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend of your website to improve its performance and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site.
Check Your Robot.txt File
As mentioned earlier, the robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. Ensuring this file is properly configured is crucial for effective SEO.
Tips for Optimizing Your Robots.txt File:
Avoid Blocking Important Pages: Make sure that your critical pages (like your homepage, product pages, etc.) are not being blocked.
Allow Access to Important Resources: Ensure that search engines can access CSS, JavaScript, and other important resources that affect how your site is displayed.
Optimize Your Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that Google considers important for user experience, including page load time, interactivity, and visual stability.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Improve your LCP by optimizing images, using fast web hosting, and enabling browser caching.
First Input Delay (FID): Reduce FID by minimizing JavaScript, using a content delivery network (CDN), and deferring unused CSS.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Minimize CLS by specifying image dimensions, avoiding ads that shift content, and ensuring fonts load properly.
Setup HTTPS
HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP, which ensures that data sent between your website and users is encrypted. Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal, so it’s important to have an SSL certificate installed on your site.
Steps to Setup HTTPS:
Purchase an SSL Certificate: You can buy an SSL certificate from your web host or a third-party provider.
Install the SSL Certificate: Follow your web host’s instructions to install the SSL certificate on your server.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure that all traffic to your site is redirected from HTTP to HTTPS using 301 redirects.
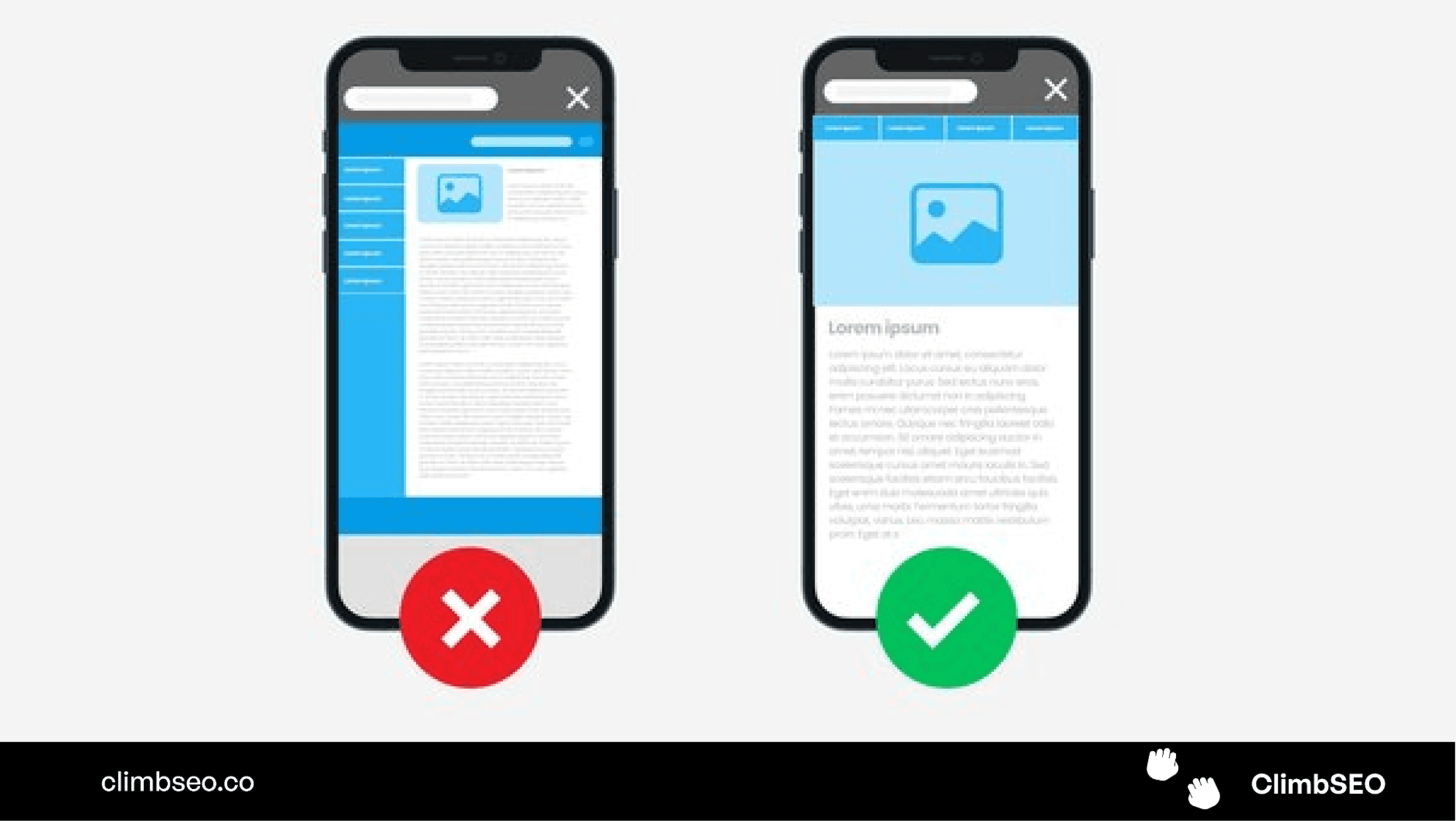
Mobile SEO: Optimizing for Mobile Users
With the majority of web traffic now coming from mobile devices, optimizing your site for mobile is more important than ever.
Mobile-Friendly Design
A mobile-friendly design is one that adapts to different screen sizes, ensuring that your site looks good and functions well on all devices.
How to Achieve Mobile-Friendly Design:
Use Responsive Design: A responsive design automatically adjusts to fit any screen size.
Simplify Navigation: Mobile users should be able to easily navigate your site with their fingers, so keep menus simple and avoid tiny links.
Optimize Images: Compress images to reduce load times and ensure they display correctly on smaller screens.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
AMP is a framework that allows you to create mobile pages that load almost instantly. While it’s not necessary for every website, implementing AMP can improve load times and provide a better user experience on mobile devices.
Benefits of AMP:
Faster Load Times: AMP pages load quickly, reducing bounce rates and improving user engagement.
Improved Mobile Rankings: Google prioritizes AMP pages in mobile search results, which can lead to higher rankings.
Measuring SEO Success
Once you’ve implemented your SEO strategy, it’s important to track your progress and measure your success. This will help you understand what’s working, what’s not, and where you can make improvements.
Organic Search Traffic
Organic traffic refers to visitors who find your site through search engines. Monitoring your organic traffic will help you understand the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
Tools to Measure Organic Traffic: Google Analytics is a powerful tool that allows you to track how much traffic your site is receiving from organic search.
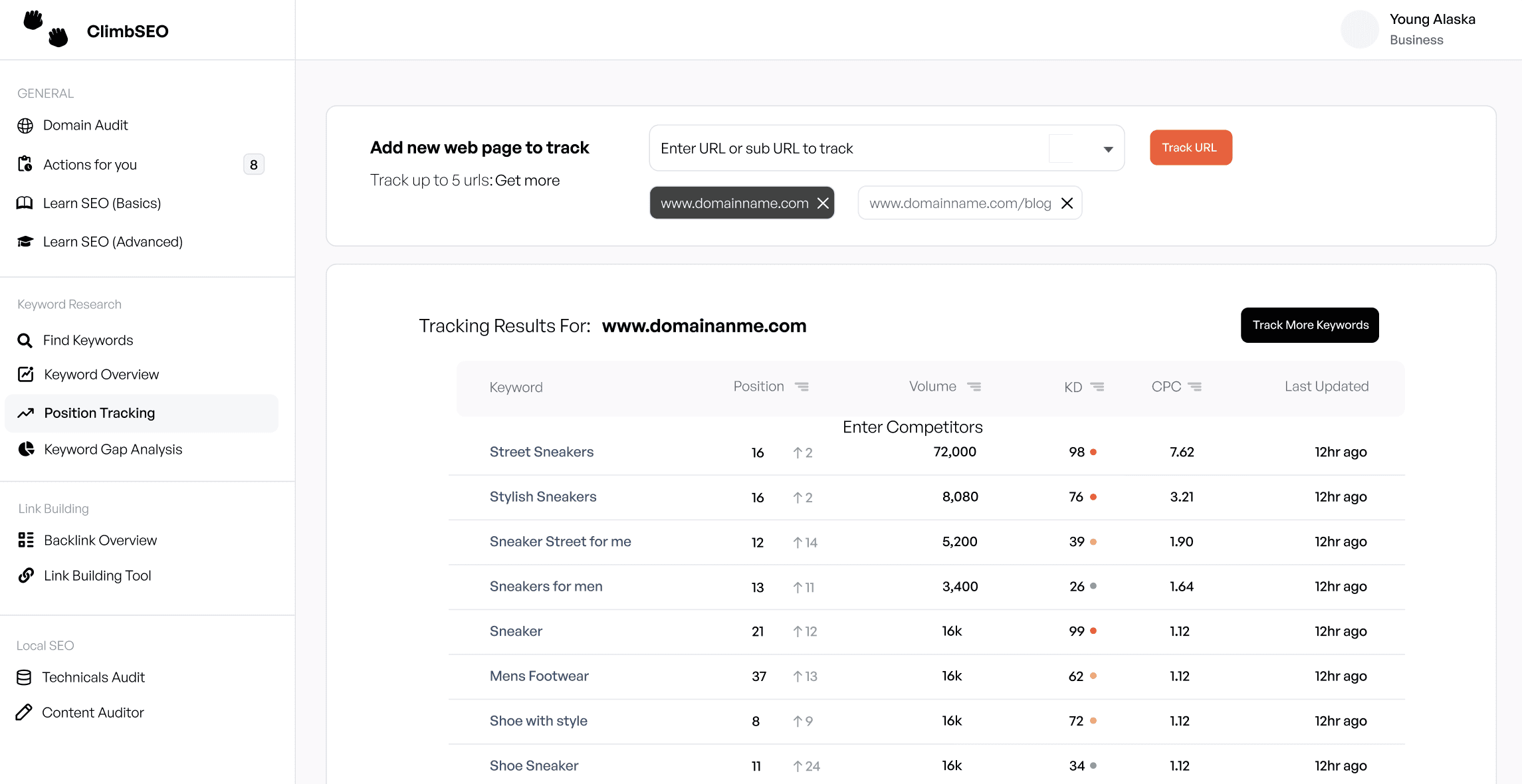
Keyword Rankings
Tracking your keyword rankings helps you see how well your site is performing for your target keywords. This will show you if your SEO efforts are paying off or if you need to adjust your strategy.
How to Track Keyword Rankings: Use tools like ClimbSEO's keyword research tool to monitor your rankings over time.
Engagement Rate and Bounce Rate
Engagement rate refers to how much time users spend on your site and how many pages they visit. Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. Both metrics are important for understanding how engaging and relevant your content is.
Tips for Improving Engagement: To keep users on your site longer, create high-quality, engaging content, and make it easy for them to find related content through internal linking.
Conversions
Ultimately, the success of your SEO efforts should be measured by how well they convert visitors into customers. Track conversion rates for key actions like making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.
How to Measure Conversions: Use Google Analytics to set up conversion goals and track how many visitors complete the desired actions on your site.
Final Thoughts
SEO may seem complex, but by following the principles outlined in this guide, you can start optimizing your website step by step. Whether you’re just beginning or looking to refine your existing strategy, understanding the basics of SEO and implementing these best practices will set you on the path to greater visibility, more traffic, and ultimately, more success for your small business.
Remember, SEO is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regularly monitor your progress, stay up-to-date with the latest trends and algorithm changes, and continuously improve your site to stay ahead of the competition. By doing so, you’ll build a strong foundation for your online presence and ensure long-term growth.
This comprehensive guide, tailored for beginners, will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to confidently navigate the world of SEO. Start today, and watch your business thrive in the digital landscape.
If you're a retail business, you might want to check this out!
We've built an e-commerce seo company for small businesses that helps you rank your products higher in Google. ClimbSEO helps you find better product keywords, understand your competitors deeper, write better product descriptions and build an all rounded e-commerce SEO strategy.
We use SemRush data, so you get all the same data points and insights in SemRush for a fraction of the price. (£49p/m compared to £129p/m)

Check our blog to find out more!
More articles like this:
SEO for E-Commerce: A Step-by-Step Guide
Best SEO Companies For Small Businesses
If you're a small business owner just stepping into the world of digital marketing, you've probably heard about SEO. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing your website so that it appears higher in search engine results, attracting more organic (non-paid) traffic. While SEO might seem intimidating at first, it’s a crucial tool for growing your online presence and driving business success.
This guide is designed as an easy-to-understand introduction to SEO, perfect for beginners. We’ll walk you through the basics, explain the key principles of SEO, and provide you with a step-by-step manual to get started. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation in SEO and be ready to start optimizing your own website.
What Is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of making your website more attractive to search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. When your site is optimized, search engines can better understand your content, index your pages, and rank your site higher in search results for relevant queries.
Key Components of SEO
On-Page SEO: Refers to the elements on your website that you can control, such as content, title tags, meta descriptions, and images.
Off-Page SEO: Involves activities outside your website that impact your rankings, such as backlinks from other websites, social media marketing, and guest blogging.
Technical SEO: Focuses on the backend of your website, including site speed, mobile-friendliness, and proper use of robots.txt and sitemaps.
Why Is SEO Important?
In today’s digital age, most consumers start their purchasing journey with an online search. If your website doesn’t appear on the first page of search results, you’re missing out on valuable traffic and potential customers. SEO is important because it helps your website get discovered by search engines, making it easier for customers to find you.
Benefits of SEO
Increased Visibility: Higher rankings mean more visibility, leading to increased traffic to your website.
Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank high in search results are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
Cost-Effective: Unlike paid advertising, organic traffic generated through SEO is free, making it a cost-effective strategy for small businesses.
Long-Term Results: While SEO takes time to show results, the benefits are long-lasting, providing continuous traffic and leads over time.
SEO 101: Ensuring Google Can Index Your Site
Before diving into more advanced SEO techniques, it’s crucial to ensure that your website is accessible to search engines. If search engines can’t find and index your site, all other SEO efforts will be in vain.
Step 1: Create and Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines understand your site’s structure and index it more efficiently.
How to Create a Sitemap: Most website platforms like WordPress or Shopify automatically generate a sitemap. If not, you can use tools like Screaming Frog or Google XML Sitemaps to create one.
Submitting Your Sitemap: Once your sitemap is ready, submit it to Google Search Console. This tells Google to crawl and index your website.

Step 2: Check Your Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is a simple text file that tells search engines which pages on your site they should or shouldn’t crawl. Ensure that this file is correctly configured to avoid accidentally blocking important pages from being indexed.
How to Access Your Robots.txt File: You can find this file at the root of your domain (e.g., www.yoursite.com/robots.txt). Check it to ensure that it’s not disallowing any critical pages.
Step 3: Ensure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
With more than half of all web traffic coming from mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your site is optimized for mobile users. If not, consider switching to a responsive design that automatically adjusts to different screen sizes.
Keyword Research: The Foundation of SEO
Keywords are the phrases that users type into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing these search terms to understand what your target audience is searching for.
Step 1: Identify Relevant Keywords
Start by brainstorming a list of words and phrases related to your business. These should include terms that describe your products or services, as well as any related topics your customers might be interested in.
Tools for Keyword Research: Use ClimbSEO's Keyword Research Tool to find out how often these keywords are searched and how competitive they are. Look for keywords with a high search volume but low competition.

Step 2: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that users are more likely to type when they’re closer to making a purchase. For example, instead of targeting “shoes,” a long-tail keyword would be “women’s running shoes for flat feet.”
Why Long-Tail Keywords Matter: They may have lower search volumes, but they’re also less competitive and often result in higher conversion rates because they match user intent more precisely.
Step 3: Analyze Competitor Keywords
Understanding which keywords your competitors are targeting can provide valuable insights. ClimbSEO's Competitor gap analysis tool helps to see which keywords are driving traffic to their websites and identify any gaps in your own keyword strategy.

Content: The Heart of SEO
Once you’ve identified your keywords, the next step is to create content that will rank for those keywords. Content is the foundation of SEO because it’s what search engines use to understand your site and decide where it should rank.
Understand What Searchers Want to See for a Query
Before creating content, it’s essential to understand search intent. This means figuring out what users are actually looking for when they type in a particular keyword.
Types of Search Intent:
Informational: The user is looking for information or answers to a question.
Navigational: The user is trying to find a specific website or page.
Transactional: The user is looking to make a purchase or take a specific action.
How to Match Search Intent: Once you understand the intent behind a keyword, create content that directly answers the user’s query. For example, if the keyword is “how to tie a tie,” a step-by-step guide with images or a video would be ideal.
Create Content That’s the Best of Its Kind
To rank well, your content needs to be better than what’s already out there. This doesn’t just mean writing more words; it means providing more value to the reader.
How to Create High-Quality Content:
Be Comprehensive: Cover all aspects of the topic in detail.
Use Visuals: Include images, infographics, and videos to make your content more engaging.
Cite Reliable Sources: Linking to credible sources can enhance your content’s authority.
Optimize Your Above-the-Fold Section
The above-the-fold section is the part of your webpage that users see without scrolling. It’s crucial to optimize this area because it’s the first thing visitors (and search engines) see.
Tips for Optimization:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Make sure your main keyword is in the headline or the first paragraph.
Use a Compelling CTA: A strong call-to-action (CTA) encourages users to stay on your page and explore further.
Ensure Fast Load Times: Slow load times can lead to higher bounce rates. Compress images and use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up your site.

User Experience: Keeping Visitors Engaged
Search engines like Google consider user experience (UX) as a ranking factor. If users have a positive experience on your site, they’re more likely to stay longer, which signals to search engines that your content is valuable.
Use Enticing CTAs
A CTA is a prompt that encourages users to take a specific action, such as “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up.” Effective CTAs are clear, compelling, and relevant to the user’s needs.
How to Create Effective CTAs:
Be Specific: Instead of “Click Here,” use “Download the Free Guide” or “Start Your Free Trial.”
Create Urgency: Phrases like “Limited Time Offer” or “Get It Now” can motivate users to act quickly.
Place Strategically: Place CTAs in prominent positions where users are most likely to see them, such as at the end of a blog post or in the middle of a product page.
Avoid Walls of Text
Large blocks of text can be intimidating and difficult to read. Break up your content into smaller paragraphs, use headings and subheadings, and incorporate bullet points and numbered lists to make it more digestible.
Tips for Readable Content:
Use Short Paragraphs: Aim for 2-3 sentences per paragraph.
Add White Space: Don’t overcrowd your pages; use white space to give your content room to breathe.
Use Images: Visual elements can help break up text and keep readers engaged.
Use Listicles, Bullets, and Numbered Lists
Listicles and bullet points are effective ways to present information because they’re easy to scan. Users can quickly find the information they’re looking for without having to read through large blocks of text.
Benefits of Lists:
Improved Readability: Lists make it easier for users to process information.
SEO Advantage: Search engines often feature listicles and bullet points in “People Also Ask” and featured snippets.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing Individual Pages
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This includes optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content for your target keywords.
Title Tags
The title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO elements. It’s the clickable headline that appears in search engine results and tells both users and search engines what the page is about.
Best Practices for Title Tags:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Place it near the beginning of the title.
Keep It Under 60 Characters: This ensures it doesn’t get cut off in search results.
Make It Compelling: Use action words and numbers to make your title more enticing (e.g., “10 Easy Tips to Improve Your SEO”).
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a brief summary of a page’s content that appears below the title tag in search results. While it doesn’t directly impact rankings, a well-written meta description can improve your click-through rate (CTR).
How to Write Effective Meta Descriptions:
Include Your Primary Keyword: This helps users quickly understand the relevance of your page.
Keep It Concise: Aim for 150-160 characters.
Use a Call-to-Action: Encourage users to click with phrases like “Learn More,” “Get Started,” or “Read On.”
Heading Tags
Heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are used to structure your content and make it easier for users to read. They also help search engines understand the hierarchy of your content.
Tips for Using Heading Tags:
Use Only One H1 Tag: This should be the main title of your page.
Incorporate Keywords: Use relevant keywords in your H2 and H3 tags to reinforce your content’s topic.
Maintain Logical Structure: Ensure your headings follow a logical order, with H1 as the main title and subsequent headings as subtopics.
Page URLs
A clean, descriptive URL structure can improve both user experience and search engine rankings. URLs should be simple, easy to read, and include your target keywords.
Best Practices for URLs:
Keep It Short: Shorter URLs are easier to remember and share.
Include Keywords: Make sure your primary keyword is part of the URL.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Avoid using underscores or spaces.
Images
Images are an essential part of any webpage, but they also need to be optimized for SEO. This includes using relevant file names, alt text, and compressing images for faster load times.
How to Optimize Images for SEO:
Use Descriptive File Names: Rename your image files to include relevant keywords (e.g., “blue-widgets.jpg” instead of “IMG_1234.jpg”).
Add Alt Text: Alt text helps search engines understand what the image is about and improves accessibility for users with visual impairments.
Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without compromising quality, improving page load times.
Adding Links from Other Pages on Your Site
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and can also pass authority from one page to another.
Best Practices for Internal Linking:
Use Descriptive Anchor Text: The clickable text of the link should describe what the linked page is about.
Link to Relevant Content: Only link to pages that are relevant to the topic at hand.
Keep a Logical Flow: Ensure that the links guide users naturally through your content.
Link Building: Strengthening Your Site’s Authority
Link building is the process of acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your own. These links are like votes of confidence from other sites, signaling to search engines that your content is trustworthy and valuable.
1. Build Links from Associations, Suppliers, and Connected Businesses
One of the easiest ways to start building links is by reaching out to associations, suppliers, and businesses you’re connected with. They may be willing to link to your website on their “Partners” or “Resources” pages.
How to Approach Link Building:
Create a List: Identify all the associations, suppliers, and partners you work with.
Reach Out: Send a polite email asking if they’d be willing to add a link to your website.
Offer Something in Return: You could offer to feature them on your site as well, making it a mutually beneficial exchange.
2. Submit Your Site to Quality Directories
Online directories can be a valuable source of backlinks, especially if they are well-respected in your industry. However, avoid low-quality directories that might be considered spammy by search engines.
Best Practices for Directory Submission:
Choose Reputable Directories: Focus on directories that are relevant to your industry and have a strong reputation.
Fill Out Your Profile Completely: Ensure that your business name, address, phone number, and website are correctly listed.
Monitor Your Listings: Regularly check your listings to ensure that the information remains accurate and up-to-date.
3. Use HARO to Earn Links from the Press
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) is a platform that connects journalists with sources for their stories. By responding to relevant queries, you can earn high-quality backlinks from authoritative media outlets.
How to Use HARO:
Sign Up: Register as a source on HARO and select the categories relevant to your business.
Monitor Queries: You’ll receive daily emails with queries from journalists looking for sources.
Respond Promptly: When you see a relevant query, respond quickly with valuable insights or expertise. If the journalist uses your information, they’ll often include a link to your website in their article.
Technical SEO: Optimizing Your Site’s Backend
Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend of your website to improve its performance and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site.
Check Your Robot.txt File
As mentioned earlier, the robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. Ensuring this file is properly configured is crucial for effective SEO.
Tips for Optimizing Your Robots.txt File:
Avoid Blocking Important Pages: Make sure that your critical pages (like your homepage, product pages, etc.) are not being blocked.
Allow Access to Important Resources: Ensure that search engines can access CSS, JavaScript, and other important resources that affect how your site is displayed.
Optimize Your Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that Google considers important for user experience, including page load time, interactivity, and visual stability.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Improve your LCP by optimizing images, using fast web hosting, and enabling browser caching.
First Input Delay (FID): Reduce FID by minimizing JavaScript, using a content delivery network (CDN), and deferring unused CSS.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Minimize CLS by specifying image dimensions, avoiding ads that shift content, and ensuring fonts load properly.
Setup HTTPS
HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP, which ensures that data sent between your website and users is encrypted. Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal, so it’s important to have an SSL certificate installed on your site.
Steps to Setup HTTPS:
Purchase an SSL Certificate: You can buy an SSL certificate from your web host or a third-party provider.
Install the SSL Certificate: Follow your web host’s instructions to install the SSL certificate on your server.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure that all traffic to your site is redirected from HTTP to HTTPS using 301 redirects.
Mobile SEO: Optimizing for Mobile Users
With the majority of web traffic now coming from mobile devices, optimizing your site for mobile is more important than ever.
Mobile-Friendly Design
A mobile-friendly design is one that adapts to different screen sizes, ensuring that your site looks good and functions well on all devices.
How to Achieve Mobile-Friendly Design:
Use Responsive Design: A responsive design automatically adjusts to fit any screen size.
Simplify Navigation: Mobile users should be able to easily navigate your site with their fingers, so keep menus simple and avoid tiny links.
Optimize Images: Compress images to reduce load times and ensure they display correctly on smaller screens.

Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
AMP is a framework that allows you to create mobile pages that load almost instantly. While it’s not necessary for every website, implementing AMP can improve load times and provide a better user experience on mobile devices.
Benefits of AMP:
Faster Load Times: AMP pages load quickly, reducing bounce rates and improving user engagement.
Improved Mobile Rankings: Google prioritizes AMP pages in mobile search results, which can lead to higher rankings.
Measuring SEO Success
Once you’ve implemented your SEO strategy, it’s important to track your progress and measure your success. This will help you understand what’s working, what’s not, and where you can make improvements.
Organic Search Traffic
Organic traffic refers to visitors who find your site through search engines. Monitoring your organic traffic will help you understand the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
Tools to Measure Organic Traffic: Google Analytics is a powerful tool that allows you to track how much traffic your site is receiving from organic search.
Keyword Rankings
Tracking your keyword rankings helps you see how well your site is performing for your target keywords. This will show you if your SEO efforts are paying off or if you need to adjust your strategy.
How to Track Keyword Rankings: Use tools like ClimbSEO's keyword research tool to monitor your rankings over time.

Engagement Rate and Bounce Rate
Engagement rate refers to how much time users spend on your site and how many pages they visit. Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. Both metrics are important for understanding how engaging and relevant your content is.
Tips for Improving Engagement: To keep users on your site longer, create high-quality, engaging content, and make it easy for them to find related content through internal linking.
Conversions
Ultimately, the success of your SEO efforts should be measured by how well they convert visitors into customers. Track conversion rates for key actions like making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.
How to Measure Conversions: Use Google Analytics to set up conversion goals and track how many visitors complete the desired actions on your site.
Final Thoughts
SEO may seem complex, but by following the principles outlined in this guide, you can start optimizing your website step by step. Whether you’re just beginning or looking to refine your existing strategy, understanding the basics of SEO and implementing these best practices will set you on the path to greater visibility, more traffic, and ultimately, more success for your small business.
Remember, SEO is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regularly monitor your progress, stay up-to-date with the latest trends and algorithm changes, and continuously improve your site to stay ahead of the competition. By doing so, you’ll build a strong foundation for your online presence and ensure long-term growth.
This comprehensive guide, tailored for beginners, will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to confidently navigate the world of SEO. Start today, and watch your business thrive in the digital landscape.
If you're a retail business, you might want to check this out!
We've built an e-commerce seo company for small businesses that helps you rank your products higher in Google. ClimbSEO helps you find better product keywords, understand your competitors deeper, write better product descriptions and build an all rounded e-commerce SEO strategy.
We use SemRush data, so you get all the same data points and insights in SemRush for a fraction of the price. (£49p/m compared to £129p/m)

Check our blog to find out more!
More articles like this:
SEO for E-Commerce: A Step-by-Step Guide
Best SEO Companies For Small Businesses
If you're a small business owner just stepping into the world of digital marketing, you've probably heard about SEO. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing your website so that it appears higher in search engine results, attracting more organic (non-paid) traffic. While SEO might seem intimidating at first, it’s a crucial tool for growing your online presence and driving business success.
This guide is designed as an easy-to-understand introduction to SEO, perfect for beginners. We’ll walk you through the basics, explain the key principles of SEO, and provide you with a step-by-step manual to get started. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation in SEO and be ready to start optimizing your own website.
What Is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of making your website more attractive to search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. When your site is optimized, search engines can better understand your content, index your pages, and rank your site higher in search results for relevant queries.
Key Components of SEO
On-Page SEO: Refers to the elements on your website that you can control, such as content, title tags, meta descriptions, and images.
Off-Page SEO: Involves activities outside your website that impact your rankings, such as backlinks from other websites, social media marketing, and guest blogging.
Technical SEO: Focuses on the backend of your website, including site speed, mobile-friendliness, and proper use of robots.txt and sitemaps.
Why Is SEO Important?
In today’s digital age, most consumers start their purchasing journey with an online search. If your website doesn’t appear on the first page of search results, you’re missing out on valuable traffic and potential customers. SEO is important because it helps your website get discovered by search engines, making it easier for customers to find you.
Benefits of SEO
Increased Visibility: Higher rankings mean more visibility, leading to increased traffic to your website.
Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank high in search results are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
Cost-Effective: Unlike paid advertising, organic traffic generated through SEO is free, making it a cost-effective strategy for small businesses.
Long-Term Results: While SEO takes time to show results, the benefits are long-lasting, providing continuous traffic and leads over time.
SEO 101: Ensuring Google Can Index Your Site
Before diving into more advanced SEO techniques, it’s crucial to ensure that your website is accessible to search engines. If search engines can’t find and index your site, all other SEO efforts will be in vain.
Step 1: Create and Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines understand your site’s structure and index it more efficiently.
How to Create a Sitemap: Most website platforms like WordPress or Shopify automatically generate a sitemap. If not, you can use tools like Screaming Frog or Google XML Sitemaps to create one.
Submitting Your Sitemap: Once your sitemap is ready, submit it to Google Search Console. This tells Google to crawl and index your website.

Step 2: Check Your Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is a simple text file that tells search engines which pages on your site they should or shouldn’t crawl. Ensure that this file is correctly configured to avoid accidentally blocking important pages from being indexed.
How to Access Your Robots.txt File: You can find this file at the root of your domain (e.g., www.yoursite.com/robots.txt). Check it to ensure that it’s not disallowing any critical pages.
Step 3: Ensure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
With more than half of all web traffic coming from mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your site is optimized for mobile users. If not, consider switching to a responsive design that automatically adjusts to different screen sizes.
Keyword Research: The Foundation of SEO
Keywords are the phrases that users type into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing these search terms to understand what your target audience is searching for.
Step 1: Identify Relevant Keywords
Start by brainstorming a list of words and phrases related to your business. These should include terms that describe your products or services, as well as any related topics your customers might be interested in.
Tools for Keyword Research: Use ClimbSEO's Keyword Research Tool to find out how often these keywords are searched and how competitive they are. Look for keywords with a high search volume but low competition.

Step 2: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that users are more likely to type when they’re closer to making a purchase. For example, instead of targeting “shoes,” a long-tail keyword would be “women’s running shoes for flat feet.”
Why Long-Tail Keywords Matter: They may have lower search volumes, but they’re also less competitive and often result in higher conversion rates because they match user intent more precisely.
Step 3: Analyze Competitor Keywords
Understanding which keywords your competitors are targeting can provide valuable insights. ClimbSEO's Competitor gap analysis tool helps to see which keywords are driving traffic to their websites and identify any gaps in your own keyword strategy.

Content: The Heart of SEO
Once you’ve identified your keywords, the next step is to create content that will rank for those keywords. Content is the foundation of SEO because it’s what search engines use to understand your site and decide where it should rank.
Understand What Searchers Want to See for a Query
Before creating content, it’s essential to understand search intent. This means figuring out what users are actually looking for when they type in a particular keyword.
Types of Search Intent:
Informational: The user is looking for information or answers to a question.
Navigational: The user is trying to find a specific website or page.
Transactional: The user is looking to make a purchase or take a specific action.
How to Match Search Intent: Once you understand the intent behind a keyword, create content that directly answers the user’s query. For example, if the keyword is “how to tie a tie,” a step-by-step guide with images or a video would be ideal.
Create Content That’s the Best of Its Kind
To rank well, your content needs to be better than what’s already out there. This doesn’t just mean writing more words; it means providing more value to the reader.
How to Create High-Quality Content:
Be Comprehensive: Cover all aspects of the topic in detail.
Use Visuals: Include images, infographics, and videos to make your content more engaging.
Cite Reliable Sources: Linking to credible sources can enhance your content’s authority.
Optimize Your Above-the-Fold Section
The above-the-fold section is the part of your webpage that users see without scrolling. It’s crucial to optimize this area because it’s the first thing visitors (and search engines) see.
Tips for Optimization:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Make sure your main keyword is in the headline or the first paragraph.
Use a Compelling CTA: A strong call-to-action (CTA) encourages users to stay on your page and explore further.
Ensure Fast Load Times: Slow load times can lead to higher bounce rates. Compress images and use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up your site.

User Experience: Keeping Visitors Engaged
Search engines like Google consider user experience (UX) as a ranking factor. If users have a positive experience on your site, they’re more likely to stay longer, which signals to search engines that your content is valuable.
Use Enticing CTAs
A CTA is a prompt that encourages users to take a specific action, such as “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up.” Effective CTAs are clear, compelling, and relevant to the user’s needs.
How to Create Effective CTAs:
Be Specific: Instead of “Click Here,” use “Download the Free Guide” or “Start Your Free Trial.”
Create Urgency: Phrases like “Limited Time Offer” or “Get It Now” can motivate users to act quickly.
Place Strategically: Place CTAs in prominent positions where users are most likely to see them, such as at the end of a blog post or in the middle of a product page.
Avoid Walls of Text
Large blocks of text can be intimidating and difficult to read. Break up your content into smaller paragraphs, use headings and subheadings, and incorporate bullet points and numbered lists to make it more digestible.
Tips for Readable Content:
Use Short Paragraphs: Aim for 2-3 sentences per paragraph.
Add White Space: Don’t overcrowd your pages; use white space to give your content room to breathe.
Use Images: Visual elements can help break up text and keep readers engaged.
Use Listicles, Bullets, and Numbered Lists
Listicles and bullet points are effective ways to present information because they’re easy to scan. Users can quickly find the information they’re looking for without having to read through large blocks of text.
Benefits of Lists:
Improved Readability: Lists make it easier for users to process information.
SEO Advantage: Search engines often feature listicles and bullet points in “People Also Ask” and featured snippets.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing Individual Pages
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This includes optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content for your target keywords.
Title Tags
The title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO elements. It’s the clickable headline that appears in search engine results and tells both users and search engines what the page is about.
Best Practices for Title Tags:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Place it near the beginning of the title.
Keep It Under 60 Characters: This ensures it doesn’t get cut off in search results.
Make It Compelling: Use action words and numbers to make your title more enticing (e.g., “10 Easy Tips to Improve Your SEO”).
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a brief summary of a page’s content that appears below the title tag in search results. While it doesn’t directly impact rankings, a well-written meta description can improve your click-through rate (CTR).
How to Write Effective Meta Descriptions:
Include Your Primary Keyword: This helps users quickly understand the relevance of your page.
Keep It Concise: Aim for 150-160 characters.
Use a Call-to-Action: Encourage users to click with phrases like “Learn More,” “Get Started,” or “Read On.”
Heading Tags
Heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are used to structure your content and make it easier for users to read. They also help search engines understand the hierarchy of your content.
Tips for Using Heading Tags:
Use Only One H1 Tag: This should be the main title of your page.
Incorporate Keywords: Use relevant keywords in your H2 and H3 tags to reinforce your content’s topic.
Maintain Logical Structure: Ensure your headings follow a logical order, with H1 as the main title and subsequent headings as subtopics.
Page URLs
A clean, descriptive URL structure can improve both user experience and search engine rankings. URLs should be simple, easy to read, and include your target keywords.
Best Practices for URLs:
Keep It Short: Shorter URLs are easier to remember and share.
Include Keywords: Make sure your primary keyword is part of the URL.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Avoid using underscores or spaces.
Images
Images are an essential part of any webpage, but they also need to be optimized for SEO. This includes using relevant file names, alt text, and compressing images for faster load times.
How to Optimize Images for SEO:
Use Descriptive File Names: Rename your image files to include relevant keywords (e.g., “blue-widgets.jpg” instead of “IMG_1234.jpg”).
Add Alt Text: Alt text helps search engines understand what the image is about and improves accessibility for users with visual impairments.
Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without compromising quality, improving page load times.
Adding Links from Other Pages on Your Site
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and can also pass authority from one page to another.
Best Practices for Internal Linking:
Use Descriptive Anchor Text: The clickable text of the link should describe what the linked page is about.
Link to Relevant Content: Only link to pages that are relevant to the topic at hand.
Keep a Logical Flow: Ensure that the links guide users naturally through your content.
Link Building: Strengthening Your Site’s Authority
Link building is the process of acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your own. These links are like votes of confidence from other sites, signaling to search engines that your content is trustworthy and valuable.
1. Build Links from Associations, Suppliers, and Connected Businesses
One of the easiest ways to start building links is by reaching out to associations, suppliers, and businesses you’re connected with. They may be willing to link to your website on their “Partners” or “Resources” pages.
How to Approach Link Building:
Create a List: Identify all the associations, suppliers, and partners you work with.
Reach Out: Send a polite email asking if they’d be willing to add a link to your website.
Offer Something in Return: You could offer to feature them on your site as well, making it a mutually beneficial exchange.
2. Submit Your Site to Quality Directories
Online directories can be a valuable source of backlinks, especially if they are well-respected in your industry. However, avoid low-quality directories that might be considered spammy by search engines.
Best Practices for Directory Submission:
Choose Reputable Directories: Focus on directories that are relevant to your industry and have a strong reputation.
Fill Out Your Profile Completely: Ensure that your business name, address, phone number, and website are correctly listed.
Monitor Your Listings: Regularly check your listings to ensure that the information remains accurate and up-to-date.
3. Use HARO to Earn Links from the Press
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) is a platform that connects journalists with sources for their stories. By responding to relevant queries, you can earn high-quality backlinks from authoritative media outlets.
How to Use HARO:
Sign Up: Register as a source on HARO and select the categories relevant to your business.
Monitor Queries: You’ll receive daily emails with queries from journalists looking for sources.
Respond Promptly: When you see a relevant query, respond quickly with valuable insights or expertise. If the journalist uses your information, they’ll often include a link to your website in their article.
Technical SEO: Optimizing Your Site’s Backend
Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend of your website to improve its performance and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site.
Check Your Robot.txt File
As mentioned earlier, the robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. Ensuring this file is properly configured is crucial for effective SEO.
Tips for Optimizing Your Robots.txt File:
Avoid Blocking Important Pages: Make sure that your critical pages (like your homepage, product pages, etc.) are not being blocked.
Allow Access to Important Resources: Ensure that search engines can access CSS, JavaScript, and other important resources that affect how your site is displayed.
Optimize Your Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that Google considers important for user experience, including page load time, interactivity, and visual stability.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Improve your LCP by optimizing images, using fast web hosting, and enabling browser caching.
First Input Delay (FID): Reduce FID by minimizing JavaScript, using a content delivery network (CDN), and deferring unused CSS.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Minimize CLS by specifying image dimensions, avoiding ads that shift content, and ensuring fonts load properly.
Setup HTTPS
HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP, which ensures that data sent between your website and users is encrypted. Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal, so it’s important to have an SSL certificate installed on your site.
Steps to Setup HTTPS:
Purchase an SSL Certificate: You can buy an SSL certificate from your web host or a third-party provider.
Install the SSL Certificate: Follow your web host’s instructions to install the SSL certificate on your server.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure that all traffic to your site is redirected from HTTP to HTTPS using 301 redirects.
Mobile SEO: Optimizing for Mobile Users
With the majority of web traffic now coming from mobile devices, optimizing your site for mobile is more important than ever.
Mobile-Friendly Design
A mobile-friendly design is one that adapts to different screen sizes, ensuring that your site looks good and functions well on all devices.
How to Achieve Mobile-Friendly Design:
Use Responsive Design: A responsive design automatically adjusts to fit any screen size.
Simplify Navigation: Mobile users should be able to easily navigate your site with their fingers, so keep menus simple and avoid tiny links.
Optimize Images: Compress images to reduce load times and ensure they display correctly on smaller screens.

Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
AMP is a framework that allows you to create mobile pages that load almost instantly. While it’s not necessary for every website, implementing AMP can improve load times and provide a better user experience on mobile devices.
Benefits of AMP:
Faster Load Times: AMP pages load quickly, reducing bounce rates and improving user engagement.
Improved Mobile Rankings: Google prioritizes AMP pages in mobile search results, which can lead to higher rankings.
Measuring SEO Success
Once you’ve implemented your SEO strategy, it’s important to track your progress and measure your success. This will help you understand what’s working, what’s not, and where you can make improvements.
Organic Search Traffic
Organic traffic refers to visitors who find your site through search engines. Monitoring your organic traffic will help you understand the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
Tools to Measure Organic Traffic: Google Analytics is a powerful tool that allows you to track how much traffic your site is receiving from organic search.
Keyword Rankings
Tracking your keyword rankings helps you see how well your site is performing for your target keywords. This will show you if your SEO efforts are paying off or if you need to adjust your strategy.
How to Track Keyword Rankings: Use tools like ClimbSEO's keyword research tool to monitor your rankings over time.

Engagement Rate and Bounce Rate
Engagement rate refers to how much time users spend on your site and how many pages they visit. Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. Both metrics are important for understanding how engaging and relevant your content is.
Tips for Improving Engagement: To keep users on your site longer, create high-quality, engaging content, and make it easy for them to find related content through internal linking.
Conversions
Ultimately, the success of your SEO efforts should be measured by how well they convert visitors into customers. Track conversion rates for key actions like making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.
How to Measure Conversions: Use Google Analytics to set up conversion goals and track how many visitors complete the desired actions on your site.
Final Thoughts
SEO may seem complex, but by following the principles outlined in this guide, you can start optimizing your website step by step. Whether you’re just beginning or looking to refine your existing strategy, understanding the basics of SEO and implementing these best practices will set you on the path to greater visibility, more traffic, and ultimately, more success for your small business.
Remember, SEO is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regularly monitor your progress, stay up-to-date with the latest trends and algorithm changes, and continuously improve your site to stay ahead of the competition. By doing so, you’ll build a strong foundation for your online presence and ensure long-term growth.
This comprehensive guide, tailored for beginners, will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to confidently navigate the world of SEO. Start today, and watch your business thrive in the digital landscape.
If you're a retail business, you might want to check this out!
We've built an e-commerce seo company for small businesses that helps you rank your products higher in Google. ClimbSEO helps you find better product keywords, understand your competitors deeper, write better product descriptions and build an all rounded e-commerce SEO strategy.
We use SemRush data, so you get all the same data points and insights in SemRush for a fraction of the price. (£49p/m compared to £129p/m)

Check our blog to find out more!
More articles like this:
SEO for E-Commerce: A Step-by-Step Guide
Best SEO Companies For Small Businesses
If you're a small business owner just stepping into the world of digital marketing, you've probably heard about SEO. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing your website so that it appears higher in search engine results, attracting more organic (non-paid) traffic. While SEO might seem intimidating at first, it’s a crucial tool for growing your online presence and driving business success.
This guide is designed as an easy-to-understand introduction to SEO, perfect for beginners. We’ll walk you through the basics, explain the key principles of SEO, and provide you with a step-by-step manual to get started. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation in SEO and be ready to start optimizing your own website.
What Is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of making your website more attractive to search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. When your site is optimized, search engines can better understand your content, index your pages, and rank your site higher in search results for relevant queries.
Key Components of SEO
On-Page SEO: Refers to the elements on your website that you can control, such as content, title tags, meta descriptions, and images.
Off-Page SEO: Involves activities outside your website that impact your rankings, such as backlinks from other websites, social media marketing, and guest blogging.
Technical SEO: Focuses on the backend of your website, including site speed, mobile-friendliness, and proper use of robots.txt and sitemaps.
Why Is SEO Important?
In today’s digital age, most consumers start their purchasing journey with an online search. If your website doesn’t appear on the first page of search results, you’re missing out on valuable traffic and potential customers. SEO is important because it helps your website get discovered by search engines, making it easier for customers to find you.
Benefits of SEO
Increased Visibility: Higher rankings mean more visibility, leading to increased traffic to your website.
Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank high in search results are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
Cost-Effective: Unlike paid advertising, organic traffic generated through SEO is free, making it a cost-effective strategy for small businesses.
Long-Term Results: While SEO takes time to show results, the benefits are long-lasting, providing continuous traffic and leads over time.
SEO 101: Ensuring Google Can Index Your Site
Before diving into more advanced SEO techniques, it’s crucial to ensure that your website is accessible to search engines. If search engines can’t find and index your site, all other SEO efforts will be in vain.
Step 1: Create and Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines understand your site’s structure and index it more efficiently.
How to Create a Sitemap: Most website platforms like WordPress or Shopify automatically generate a sitemap. If not, you can use tools like Screaming Frog or Google XML Sitemaps to create one.
Submitting Your Sitemap: Once your sitemap is ready, submit it to Google Search Console. This tells Google to crawl and index your website.

Step 2: Check Your Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is a simple text file that tells search engines which pages on your site they should or shouldn’t crawl. Ensure that this file is correctly configured to avoid accidentally blocking important pages from being indexed.
How to Access Your Robots.txt File: You can find this file at the root of your domain (e.g., www.yoursite.com/robots.txt). Check it to ensure that it’s not disallowing any critical pages.
Step 3: Ensure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
With more than half of all web traffic coming from mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check if your site is optimized for mobile users. If not, consider switching to a responsive design that automatically adjusts to different screen sizes.
Keyword Research: The Foundation of SEO
Keywords are the phrases that users type into search engines when looking for information, products, or services. Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing these search terms to understand what your target audience is searching for.
Step 1: Identify Relevant Keywords
Start by brainstorming a list of words and phrases related to your business. These should include terms that describe your products or services, as well as any related topics your customers might be interested in.
Tools for Keyword Research: Use ClimbSEO's Keyword Research Tool to find out how often these keywords are searched and how competitive they are. Look for keywords with a high search volume but low competition.

Step 2: Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that users are more likely to type when they’re closer to making a purchase. For example, instead of targeting “shoes,” a long-tail keyword would be “women’s running shoes for flat feet.”
Why Long-Tail Keywords Matter: They may have lower search volumes, but they’re also less competitive and often result in higher conversion rates because they match user intent more precisely.
Step 3: Analyze Competitor Keywords
Understanding which keywords your competitors are targeting can provide valuable insights. ClimbSEO's Competitor gap analysis tool helps to see which keywords are driving traffic to their websites and identify any gaps in your own keyword strategy.

Content: The Heart of SEO
Once you’ve identified your keywords, the next step is to create content that will rank for those keywords. Content is the foundation of SEO because it’s what search engines use to understand your site and decide where it should rank.
Understand What Searchers Want to See for a Query
Before creating content, it’s essential to understand search intent. This means figuring out what users are actually looking for when they type in a particular keyword.
Types of Search Intent:
Informational: The user is looking for information or answers to a question.
Navigational: The user is trying to find a specific website or page.
Transactional: The user is looking to make a purchase or take a specific action.
How to Match Search Intent: Once you understand the intent behind a keyword, create content that directly answers the user’s query. For example, if the keyword is “how to tie a tie,” a step-by-step guide with images or a video would be ideal.
Create Content That’s the Best of Its Kind
To rank well, your content needs to be better than what’s already out there. This doesn’t just mean writing more words; it means providing more value to the reader.
How to Create High-Quality Content:
Be Comprehensive: Cover all aspects of the topic in detail.
Use Visuals: Include images, infographics, and videos to make your content more engaging.
Cite Reliable Sources: Linking to credible sources can enhance your content’s authority.
Optimize Your Above-the-Fold Section
The above-the-fold section is the part of your webpage that users see without scrolling. It’s crucial to optimize this area because it’s the first thing visitors (and search engines) see.
Tips for Optimization:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Make sure your main keyword is in the headline or the first paragraph.
Use a Compelling CTA: A strong call-to-action (CTA) encourages users to stay on your page and explore further.
Ensure Fast Load Times: Slow load times can lead to higher bounce rates. Compress images and use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up your site.

User Experience: Keeping Visitors Engaged
Search engines like Google consider user experience (UX) as a ranking factor. If users have a positive experience on your site, they’re more likely to stay longer, which signals to search engines that your content is valuable.
Use Enticing CTAs
A CTA is a prompt that encourages users to take a specific action, such as “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up.” Effective CTAs are clear, compelling, and relevant to the user’s needs.
How to Create Effective CTAs:
Be Specific: Instead of “Click Here,” use “Download the Free Guide” or “Start Your Free Trial.”
Create Urgency: Phrases like “Limited Time Offer” or “Get It Now” can motivate users to act quickly.
Place Strategically: Place CTAs in prominent positions where users are most likely to see them, such as at the end of a blog post or in the middle of a product page.
Avoid Walls of Text
Large blocks of text can be intimidating and difficult to read. Break up your content into smaller paragraphs, use headings and subheadings, and incorporate bullet points and numbered lists to make it more digestible.
Tips for Readable Content:
Use Short Paragraphs: Aim for 2-3 sentences per paragraph.
Add White Space: Don’t overcrowd your pages; use white space to give your content room to breathe.
Use Images: Visual elements can help break up text and keep readers engaged.
Use Listicles, Bullets, and Numbered Lists
Listicles and bullet points are effective ways to present information because they’re easy to scan. Users can quickly find the information they’re looking for without having to read through large blocks of text.
Benefits of Lists:
Improved Readability: Lists make it easier for users to process information.
SEO Advantage: Search engines often feature listicles and bullet points in “People Also Ask” and featured snippets.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing Individual Pages
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. This includes optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content for your target keywords.
Title Tags
The title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO elements. It’s the clickable headline that appears in search engine results and tells both users and search engines what the page is about.
Best Practices for Title Tags:
Include Your Primary Keyword: Place it near the beginning of the title.
Keep It Under 60 Characters: This ensures it doesn’t get cut off in search results.
Make It Compelling: Use action words and numbers to make your title more enticing (e.g., “10 Easy Tips to Improve Your SEO”).
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a brief summary of a page’s content that appears below the title tag in search results. While it doesn’t directly impact rankings, a well-written meta description can improve your click-through rate (CTR).
How to Write Effective Meta Descriptions:
Include Your Primary Keyword: This helps users quickly understand the relevance of your page.
Keep It Concise: Aim for 150-160 characters.
Use a Call-to-Action: Encourage users to click with phrases like “Learn More,” “Get Started,” or “Read On.”
Heading Tags
Heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are used to structure your content and make it easier for users to read. They also help search engines understand the hierarchy of your content.
Tips for Using Heading Tags:
Use Only One H1 Tag: This should be the main title of your page.
Incorporate Keywords: Use relevant keywords in your H2 and H3 tags to reinforce your content’s topic.
Maintain Logical Structure: Ensure your headings follow a logical order, with H1 as the main title and subsequent headings as subtopics.
Page URLs
A clean, descriptive URL structure can improve both user experience and search engine rankings. URLs should be simple, easy to read, and include your target keywords.
Best Practices for URLs:
Keep It Short: Shorter URLs are easier to remember and share.
Include Keywords: Make sure your primary keyword is part of the URL.
Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Avoid using underscores or spaces.
Images
Images are an essential part of any webpage, but they also need to be optimized for SEO. This includes using relevant file names, alt text, and compressing images for faster load times.
How to Optimize Images for SEO:
Use Descriptive File Names: Rename your image files to include relevant keywords (e.g., “blue-widgets.jpg” instead of “IMG_1234.jpg”).
Add Alt Text: Alt text helps search engines understand what the image is about and improves accessibility for users with visual impairments.
Compress Images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without compromising quality, improving page load times.
Adding Links from Other Pages on Your Site
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and can also pass authority from one page to another.
Best Practices for Internal Linking:
Use Descriptive Anchor Text: The clickable text of the link should describe what the linked page is about.
Link to Relevant Content: Only link to pages that are relevant to the topic at hand.
Keep a Logical Flow: Ensure that the links guide users naturally through your content.
Link Building: Strengthening Your Site’s Authority
Link building is the process of acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your own. These links are like votes of confidence from other sites, signaling to search engines that your content is trustworthy and valuable.
1. Build Links from Associations, Suppliers, and Connected Businesses
One of the easiest ways to start building links is by reaching out to associations, suppliers, and businesses you’re connected with. They may be willing to link to your website on their “Partners” or “Resources” pages.
How to Approach Link Building:
Create a List: Identify all the associations, suppliers, and partners you work with.
Reach Out: Send a polite email asking if they’d be willing to add a link to your website.
Offer Something in Return: You could offer to feature them on your site as well, making it a mutually beneficial exchange.
2. Submit Your Site to Quality Directories
Online directories can be a valuable source of backlinks, especially if they are well-respected in your industry. However, avoid low-quality directories that might be considered spammy by search engines.
Best Practices for Directory Submission:
Choose Reputable Directories: Focus on directories that are relevant to your industry and have a strong reputation.
Fill Out Your Profile Completely: Ensure that your business name, address, phone number, and website are correctly listed.
Monitor Your Listings: Regularly check your listings to ensure that the information remains accurate and up-to-date.
3. Use HARO to Earn Links from the Press
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) is a platform that connects journalists with sources for their stories. By responding to relevant queries, you can earn high-quality backlinks from authoritative media outlets.
How to Use HARO:
Sign Up: Register as a source on HARO and select the categories relevant to your business.
Monitor Queries: You’ll receive daily emails with queries from journalists looking for sources.
Respond Promptly: When you see a relevant query, respond quickly with valuable insights or expertise. If the journalist uses your information, they’ll often include a link to your website in their article.
Technical SEO: Optimizing Your Site’s Backend
Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend of your website to improve its performance and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site.
Check Your Robot.txt File
As mentioned earlier, the robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which to ignore. Ensuring this file is properly configured is crucial for effective SEO.
Tips for Optimizing Your Robots.txt File:
Avoid Blocking Important Pages: Make sure that your critical pages (like your homepage, product pages, etc.) are not being blocked.
Allow Access to Important Resources: Ensure that search engines can access CSS, JavaScript, and other important resources that affect how your site is displayed.
Optimize Your Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that Google considers important for user experience, including page load time, interactivity, and visual stability.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Improve your LCP by optimizing images, using fast web hosting, and enabling browser caching.
First Input Delay (FID): Reduce FID by minimizing JavaScript, using a content delivery network (CDN), and deferring unused CSS.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Minimize CLS by specifying image dimensions, avoiding ads that shift content, and ensuring fonts load properly.
Setup HTTPS
HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP, which ensures that data sent between your website and users is encrypted. Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal, so it’s important to have an SSL certificate installed on your site.
Steps to Setup HTTPS:
Purchase an SSL Certificate: You can buy an SSL certificate from your web host or a third-party provider.
Install the SSL Certificate: Follow your web host’s instructions to install the SSL certificate on your server.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Ensure that all traffic to your site is redirected from HTTP to HTTPS using 301 redirects.
Mobile SEO: Optimizing for Mobile Users
With the majority of web traffic now coming from mobile devices, optimizing your site for mobile is more important than ever.
Mobile-Friendly Design
A mobile-friendly design is one that adapts to different screen sizes, ensuring that your site looks good and functions well on all devices.
How to Achieve Mobile-Friendly Design:
Use Responsive Design: A responsive design automatically adjusts to fit any screen size.
Simplify Navigation: Mobile users should be able to easily navigate your site with their fingers, so keep menus simple and avoid tiny links.
Optimize Images: Compress images to reduce load times and ensure they display correctly on smaller screens.

Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)
AMP is a framework that allows you to create mobile pages that load almost instantly. While it’s not necessary for every website, implementing AMP can improve load times and provide a better user experience on mobile devices.
Benefits of AMP:
Faster Load Times: AMP pages load quickly, reducing bounce rates and improving user engagement.
Improved Mobile Rankings: Google prioritizes AMP pages in mobile search results, which can lead to higher rankings.
Measuring SEO Success
Once you’ve implemented your SEO strategy, it’s important to track your progress and measure your success. This will help you understand what’s working, what’s not, and where you can make improvements.
Organic Search Traffic
Organic traffic refers to visitors who find your site through search engines. Monitoring your organic traffic will help you understand the effectiveness of your SEO efforts.
Tools to Measure Organic Traffic: Google Analytics is a powerful tool that allows you to track how much traffic your site is receiving from organic search.
Keyword Rankings
Tracking your keyword rankings helps you see how well your site is performing for your target keywords. This will show you if your SEO efforts are paying off or if you need to adjust your strategy.
How to Track Keyword Rankings: Use tools like ClimbSEO's keyword research tool to monitor your rankings over time.

Engagement Rate and Bounce Rate
Engagement rate refers to how much time users spend on your site and how many pages they visit. Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. Both metrics are important for understanding how engaging and relevant your content is.
Tips for Improving Engagement: To keep users on your site longer, create high-quality, engaging content, and make it easy for them to find related content through internal linking.
Conversions
Ultimately, the success of your SEO efforts should be measured by how well they convert visitors into customers. Track conversion rates for key actions like making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.
How to Measure Conversions: Use Google Analytics to set up conversion goals and track how many visitors complete the desired actions on your site.
Final Thoughts
SEO may seem complex, but by following the principles outlined in this guide, you can start optimizing your website step by step. Whether you’re just beginning or looking to refine your existing strategy, understanding the basics of SEO and implementing these best practices will set you on the path to greater visibility, more traffic, and ultimately, more success for your small business.
Remember, SEO is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regularly monitor your progress, stay up-to-date with the latest trends and algorithm changes, and continuously improve your site to stay ahead of the competition. By doing so, you’ll build a strong foundation for your online presence and ensure long-term growth.
This comprehensive guide, tailored for beginners, will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to confidently navigate the world of SEO. Start today, and watch your business thrive in the digital landscape.
If you're a retail business, you might want to check this out!
We've built an e-commerce seo company for small businesses that helps you rank your products higher in Google. ClimbSEO helps you find better product keywords, understand your competitors deeper, write better product descriptions and build an all rounded e-commerce SEO strategy.
We use SemRush data, so you get all the same data points and insights in SemRush for a fraction of the price. (£49p/m compared to £129p/m)

Check our blog to find out more!
More articles like this:
SEO for E-Commerce: A Step-by-Step Guide
Best SEO Companies For Small Businesses
Read more articles
Join Global Businesses and Unlock Your SEO Potential!
Join Global Businesses and Unlock Your SEO Potential!
Join Global Businesses and Unlock Your SEO Potential!
Join Global Businesses and Unlock Your SEO Potential!
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved by ClimbSEO
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved by ClimbSEO
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved by ClimbSEO
© Copyright 2024, All Rights Reserved by ClimbSEO